
Blockchain technology is no longer a new concept. It is a disruptive technology that is shaping various aspects of business, except for the traditional methods of doing any activity. The scope of blockchain technology extends beyond finance, payments, and information processing.
Blockchain defies the concept of centralization, in simpler terms, taking control of a business from a central authority. With its distinctive features like decentralization, transparency, and security, it is making its way into the mainstream.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a structure for transparently sharing information within a business. It has a high transparency score. Blockchain is an immutable ledger that stores data or information in the form of blocks, secured by cryptography. The capacity to process immense amounts of transactions efficiently is still one of the major problems that blockchain networks need to solve.
Types of Blockchain
- Public Blockchain: Open networks where anyone can join, validate transactions, and access the ledger.
- Private Blockchain: Permissioned networks controlled by a single organization for faster, more secure operations.
- Consortium Blockchain: Multiple entities govern these semi-decentralized networks. The infrastructure helps balance trust and efficiency in the overall network.
Key Features of Blockchain
- Transparency: The network participants can fully verify all the blockchain transactions with the exact timestamp. The blockchains have their own dedicated explorer that helps verify transaction details.
- Security: Blockchain provides security against unauthorized access, which includes the network’s data and transaction tampering.
- Immutability: The immutable nature of blockchain provides strong protection against data alteration or deletion.
- Decentralization: Decentralization empowers the whole network and doesn’t restrict the control to a single entity.
Scalability is a key factor as the networks expand, thus making the Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions necessary for handling a larger number of transactions efficiently while locking the speed and security levels.
Why Scalability Matters in Blockchain
A blockchain transaction undergoes a process of validation, confirmation, and recording on a decentralized network of nodes. Although this whole operation secures the system and keeps the data intact, it heavily drains computer resources and takes time. In the event of an increase in transaction demand, the networks may experience congestion, resulting in delays in confirmations and, consequently, a rise in transaction fees.
In contrast, the traditional payment systems can process thousands of transactions every second, but many blockchains are still having a challenging time getting even a small fraction of that throughput. The inability to scale up the infrastructure could block the use of blockchain in payments, DeFi, gaming, and digital identity, among other areas. Consequently, scalability improvement is what the technology needs to make it future-proof.
Understanding Layer 1 Blockchain Scaling
A Layer 1 blockchain is the primary blockchain that supports all major transactions and activities. It is the blockchain ecosystem’s base and can host other blockchains or apps. The main elements consist of the availability of data, consensus processes, and a distribution of nodes, which together provide the characteristics of security, decentralization, and seamless operation.
The Layer 1 scaling considers the performance of the whole blockchain by adjusting its core architecture as a main target. Common approaches include updating the consensus mechanisms, implementing sharding, and changing the block size or the block production time. Such changes can lead to a significant increase in the number of transactions processed and the overall efficiency at the protocol level.
Nevertheless, the Layer 1 updates are never easy, and they usually entail the agreement of the whole network. Once put into action, they become irreversible, which is why Layer 1 scaling is a very time-consuming process requiring extreme care.
Understanding Layer 2 Blockchain Scaling
Layer 2 solutions refer to second-level protocols that operate over already existing blockchains. They focus on the off-chain transaction processing rather than the base protocol changing, with the main network being settled by the transaction results that were finalized and submitted periodically.
The main layer of Layer 2 solutions is transaction activity that is routed to various places, which is very effective in reducing congestion and improving transaction speed and making fees lower. Some of the most well-known chains in this category are Bitcoin’s Lightning Network and Ethereum Orbiting-built ones like sidechains, state channels, and rollups.
The term “Layer 2 scaling” enables blockchain systems to handle very high transaction volumes at the same time without compromising on security and decentralization. The process ultimately provides benefits to the underlying Layer 1 network.
Key Differences Between Layer 1 and Layer 2
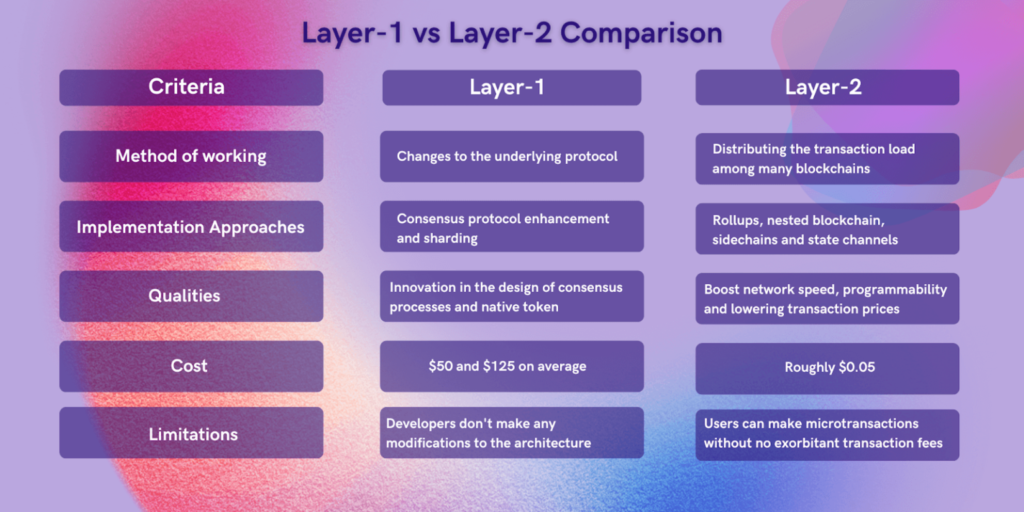
Layer 1 scaling solutions aim to improve the fundamental protocol of the blockchain. The changes made at this level will slowly show up in the network’s ability to handle transactions, reach consensus, and keep security. Since Layer 1 serves as the ultimate source of truth, executing improvements at this level can be challenging.
Layer 2 solutions, on the other hand, do not require any changes to the base blockchain and still gain the benefit of scaling. They process transactions on the so-called secondary networks or off-chain systems and use Layer 1 for settlement and obtaining security guarantees. The above method enables the network to have a greater throughput and more optimized fees, all without compromising trust in the underlying blockchain.
In this context, the first layer provides foundational power to the network, while the second layer offers flexibility and cost-effective execution.
Balancing Security, Decentralization, and Scalability
Blockchain networks must maintain a balance among their three main properties: security, decentralization, and scalability. This challenge is referred to as the scalability trilemma. It states that a blockchain shall optimize these three simultaneously, wherein two of them are possible at a time in the current state, increasing scalability usually results in lowered decentralization or security, and vice versa.
To illustrate, Bitcoin chooses security and decentralization over scalability, which in turn restricts its transaction capacity. That is why many blockchain platforms prefer Layer 2 solutions to their original principles to achieve scalability.
The Future of Blockchain Scaling
The adoption of blockchain technology is expected to experience continuous growth in the future. The scalable infrastructure remains a sought-after feature. However, neither Layer 1 nor Layer 2 solutions are fully optimized right now. Going forward, innovative thinking in consensus protocols, flexible blockchains, and off-chain execution layers will determine the next evolution cycle of blockchain technology.


