
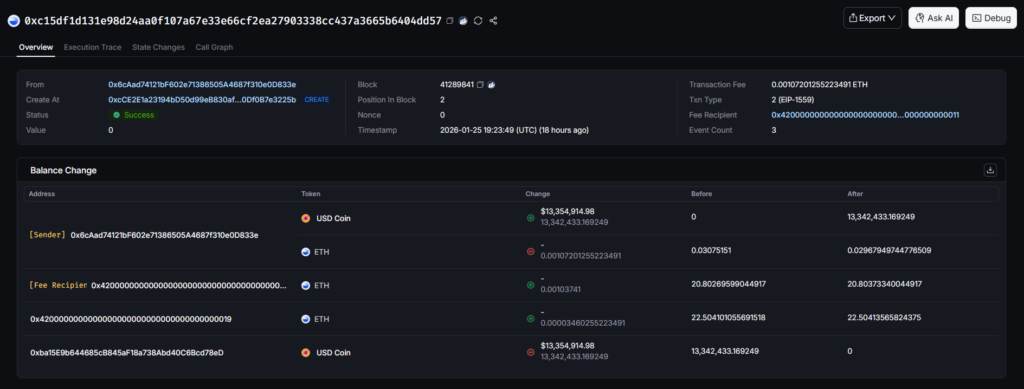
A recent DEX aggregator Matcha Meta exploit has been reported with a U$D 16.8 million value loss. The critical vulnerability was identified with the SwapNet router contract. This incident was confirmed and informed, and funds were drained from affected users who had opted out of the Matcha Meta one-time approval safety feature.
How the SwapNet Router Vulnerability Was Exploited
The attack exploited a critical, yet common, DeFi weakness: persistent token approvals. Matcha Meta offers a security feature called “0x One-Time Approval,” which only grants temporary permission for a trade. For instance, users who manually disabled this feature gave standing, unlimited approval to underlying aggregator contracts, including SwapNet.
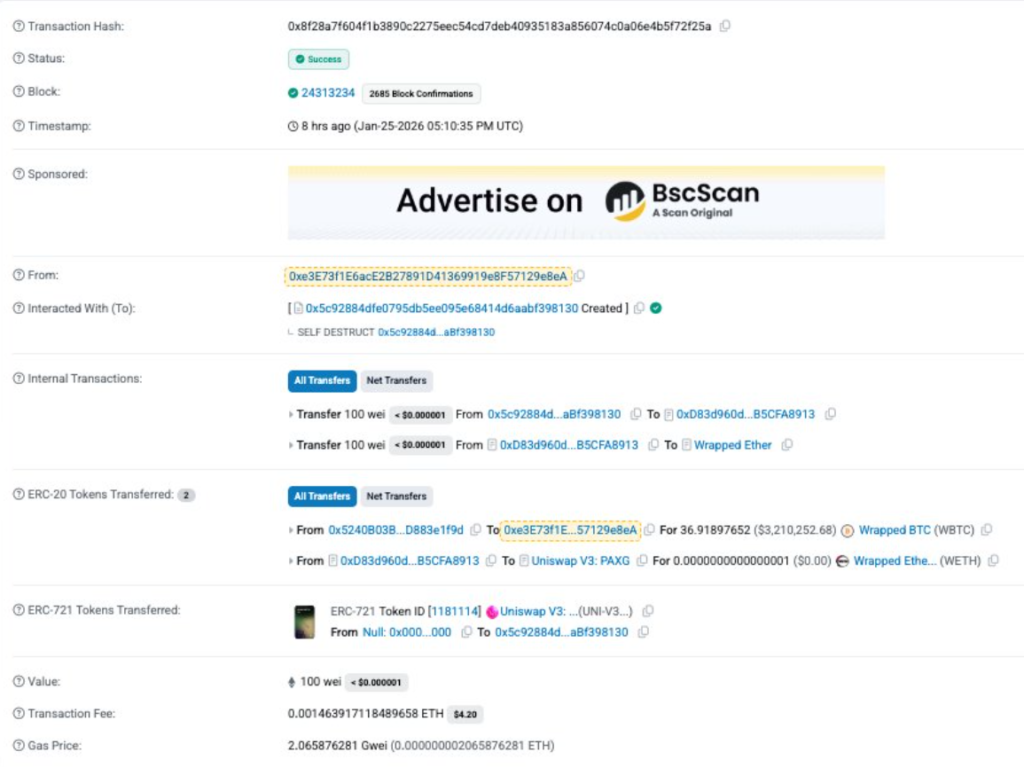
The attacker took advantage of this vulnerability found within SwapNet’s router to drain funds from user accounts that had already pre-approved wallets. After the attack took place, on-chain analysis revealed that the hacker exchanged funds for around U$D 10.5 million worth of USDC and used these funds to buy a total of 3,655 ETH on the Base platform. After purchasing the ETH, the attacker utilized a bridge to transfer stolen ETH back to the Ethereum mainnet, a typical obfuscation tactic.
Why This Incident Highlights a Systemic DeFi Risk
This Matcha Meta exploit highlights the dangers of systemic DeFi risk. The use of a third-party router by Matcha exemplifies how one weak link in a transaction path can weaken security for all users. While no direct contract was compromised in the core 0x protocol, Matcha was forced to cancel/remove the option for users to give direct access to aggregator contracts after identifying the attack.
Moreover, this action, while necessary, also highlights the tension between user control (opting out of security features) and platform-enforced safety in a permissionless DeFi ecosystem.


